
This will avoid unnecessary painting and UI delay. Traverse the non-databound list and add, edit, or remove items.
MSDN ERRORPROVIDER CODE
Rather, encapsulate a block of code with calls to BeginUpdate and EndUpdate. It will cause excessive screen painting if you use it. You also should avoid the use of Items.Clear() with non-databound lists. List = new ListViewItem("Item" + i.ToString()) Additionally, it performs other optimizations to the methods internally to ensure efficiency in the loading, as follows: ListViewItem list = new ListViewItem It automatically calls BeginUpdate and EndUpdate. You also can use the AddRange method to efficiently add an array of pre-created items. ListViewItem listItem = new ListViewItem("Item"+i.ToString() ) Here’s an example: listView1.BeginUpdate() The BeginUpdate and EndUpdate methods allow bulk operations to occur without causing excessive repainting. Loading items into controls such as ListView and TreeView causes a repainting after each change. To prevent your control from being populated multiple times, a good practice is to always set the DataSource property last on controls such as ComboBox and ListBox, as follows: comboBox1.ValueMember = "Name" This means your controls may inadvertently populate multiple times. When you change the ValueMember property on controls programmatically, it causes most controls to repopulate the data from the configured DataSource. Data Binding Optimizationĭata binding allows data to be processed automatically and displayed in controls such as ComboBox on the user interface (UI). You’ll need to have some level of familiarity with topics such as data binding and validation to follow along.
MSDN ERRORPROVIDER WINDOWS
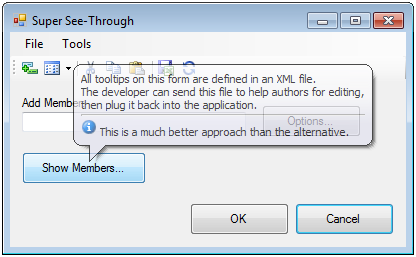
Rather than focusing on a specific feature, it covers a variety of topics that will assist you in building fully functional and well performing Windows Forms applications. (You can set the error to the control by name, or generically by using the sender argument.This article dives into Windows Forms. If the input is not valid, we set the error shown by the ErrorProvider (the e.Message is generally the same as the Message parameter of any exception that has been thrown). We also clear any errors in the ErrorProvider (not sure of the best way to use this control, but this works).

In that event handler, we check if the input is valid (don't know what all that does, but it works - play with it) and, if so, cast the value to the correct data type in order to use for some purpose. The example shows us setting the type of data which should be entered into the text box and then subscribing to the corresponding event. It's really useful when combined with the above data validation method. The ErrorProvider is a WinForms control that allows you to show a red exclamation mark with an error message tooltip next to a control. When the mask is blank, you can accept input just like you can with a TextBox.
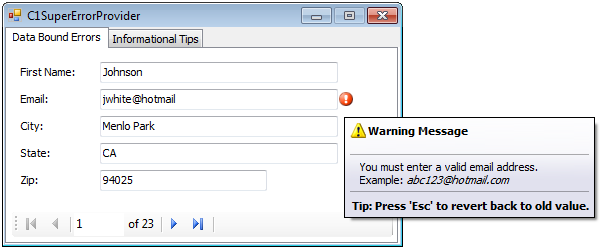
What you should be aware of, though, is that the Mask is *not* required. If you want to read about the MaskedTextBox, it's all on MSDN. If you do this, as well as subscribe to the TypeValidationCompleted event, on the form Load event, you can handle user validation inside your TypeValidationCompleted event handler. The trick is to set the ValidatingType of the MaskedTextBox control to the type of data you want to get from the user. I just discovered that the MaskedTextBox control allows you to set the type of data which should be entered in the control and helps you do the validation of that data when necessary.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
